Git & GitHub for Beginners!
This is just an introduction about Git and GitHub for those who might be interested in. In this article, you will understand what Git is and how to use it on the remote repository platforms, like GitHub. Whether you are an absolute beginner or an experienced user, you will be guided through all images and clear instructions.
Content
- What is Git?
- Install Git
- Getting Started with Git
- Git Glossary
- Git Commands
- Platforms
- What is GitHub?
- Git Vs GitHub
What is Git?

Git is an example of a distributed version Control System which is originally created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 and commenly used for open source and commercial software development.
It is,
- Free
- Open Source
- Super Fast
- Scalable
- Branching/Merging
First let’s see what is a version control system and why we need it.
It just tracks and manages all the changes and modifications to source code over time in a special database called 'Repositary'. It is a software tool that helps to software development teams to work faster and smarter with the confidence that any version can be recoverd at any time. Developers can review project history to find out which changes were made who made the changes, when were the changes made, why were changes needed. Without a version control system, for a single developer, it's already a challenge to keep track of multiple copies of a single project. Now imagine developers collaborate as teams on the same project, each developer has to email it or any other method to pass to others and then manually merge the changes.So the situation becomes worse. Therefore, using a version control system is a best practice for high performing software development teams.
The Version Control System is also categorized into two parts.
- Centralized - all team members connect to a central server to get the latest copy of the code and share the changes with others. But the problem is, if the server goes offline, team members cannot collaborate and have to wait until server comes back online.
- Distributed - every team member has a copy of the projects on their machine. If the server is offline, they can synchronized their work directly with others.
There are many ways to use Git. We can use git on the command line , code editors & IDEs , graphical user interface
Install GIT
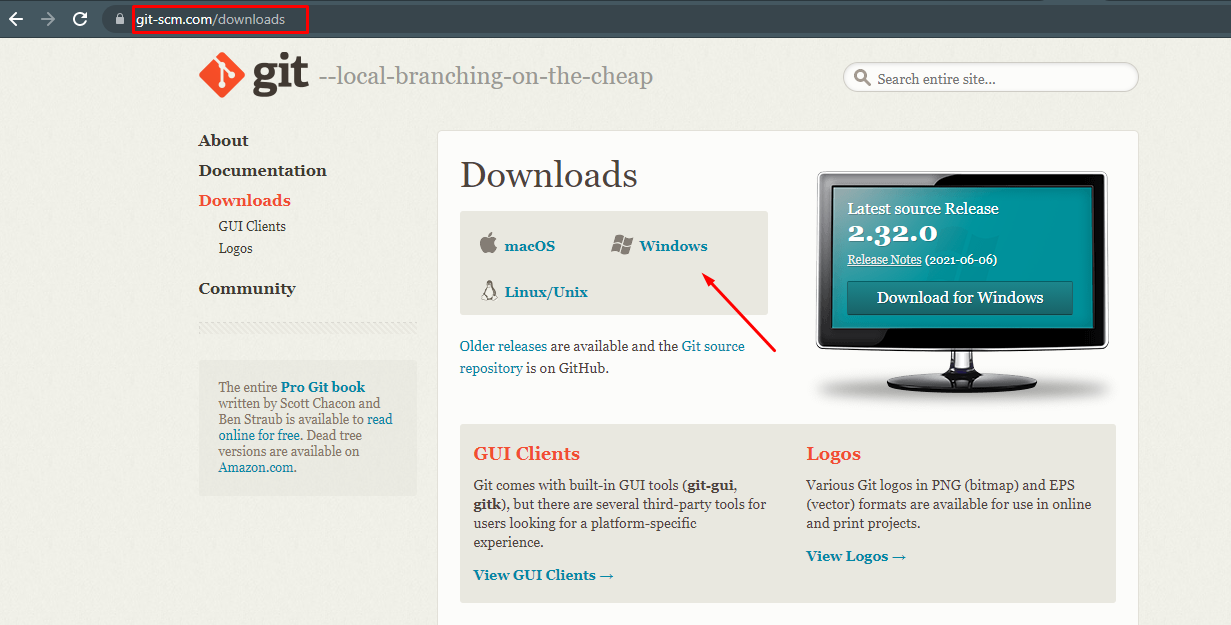
You can download Git for free and then install it.
GET STARTED WITH GIT!
Here is a basic overview of how Git works:
- Create a “repository” with a git hosting tool like GitHub.
- Copy (or clone) the repository to your local machine
- Add a file to your local repo and “commit” (save) the changes
- “Push” your changes to your main branch
- Make a change to your file with a git hosting tool and commit
- “Pull” the changes to your local machine
- Create a “branch” (version), make a change, commit the change
- Open a “pull request” (propose changes to the main branch)
- “Merge” your branch to the main branch
or there is another way too!
- If you already have a folder/directory you would like to use for Git in your local machine, Navigate to it in command line, or open it in your file explorer, right-click and select “Git Bash here”
- Once you have navigated to the correct folder, you can initialize Git on that folder.
- Then you just created your first Git Repository!
- Now you can work on your project.
Git Glossary
When we learn how to work using Git, We have met some new terms like ‘repo’,’push’,’pull’, ‘branch’, ‘clone’,’merge’ and ‘master’ etc. It’s very important to know those terms and what they exactly do. Therefore, follow the below link for more information.
Git Commands
The Essential and Basic Git Commands every developer must know.
- Creating Git Folder
mkdir projectName
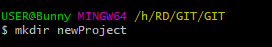
cd projectName
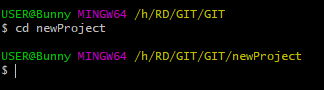
- Initialize Git
git init
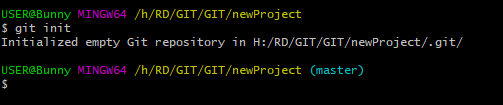
You just created your first local Git repo. But it is empty.
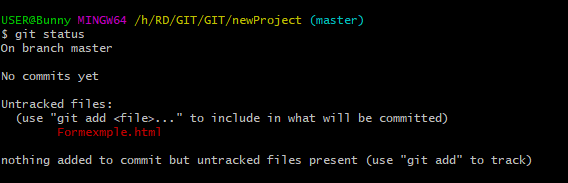
git status
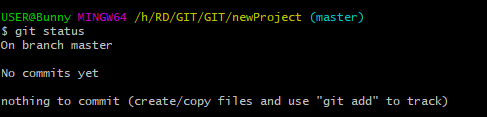
So let’s add some files, or create a new file using your favourite text editor. Then save or move it to the folder you just created.
- Add new files
ls
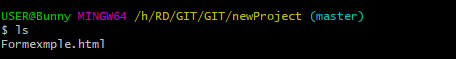
git add fileName
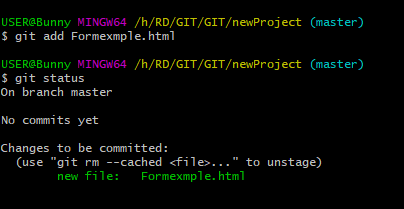
- Git Commit
To save changes
git commit -m “commit message”
- Git Commit Log
To view the history of commits for a repository
git log
- Git Branch
To work in a new version of the main repository.
git branch newFeatureBranchName
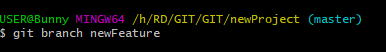
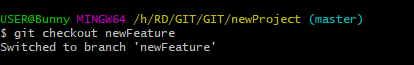
- Git Checkout
To move current workspace from the master branch, to the new branch. Then make changes.
git checkout newFeatureBranchName
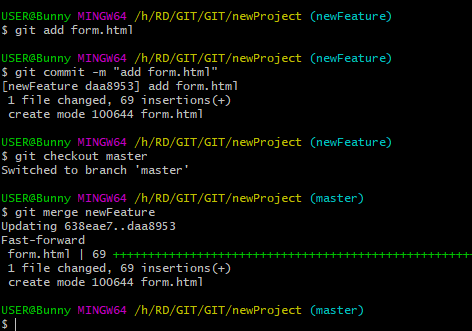
- Git Merge
After make changes, save them and merge feature branch with master branch. Before merging, Go back to the main branch.
git checkout master
git merge newFeatureBranchName
There are so many Git commands. If you are starting out, Don’t worry too much about memorizing these commands instead try to understand how they work.
You can easily follow the below link to get more help on Git Commands.
Platforms
Places to host git repository
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
- SourceForge
What is GitHub?
.png)
GitHub is a Git repository hosting service that provides a web-based graphical interface.
It is the world largest coding community. When you publish a piece of code or a project on GitHub, it gets a lot of attention. Programmers may find source codes in a variety of languages and make and track modifications using Git, a command-line interface. GitHub allows everyone on a team to work on a project from anywhere while facilitating cooperation. You can also look at prior versions that were made at a different time. GitHub is a platform for project managers and developers to collaborate, track, and update their work in order to keep projects transparent and on track.Packages can be shared privately, within the team, or publicly to the open-source community.
GET STARTED WITH GITHUB
For beginners, click on to GitHub Site and create an account.

- Configure Git
Once Git is installed, let Git know who you are. Use global to set the username and e-mail for every repository on your computer.
git config –global user.name “username on your github account”
git config –global user.email “email used in github”
Once you set your configurations as global, No need to set it again and you can check your configurations as follows:
git config –global –list
You’re now ready to use both Git and GitHub!
Git Vs GitHub

Finally, let’s see the differences between Git & GitHub!
Git & GitHub are not the same thing.
- Git is a software, that can be installed directly on to the system whereas GitHub is hosted on the cloud.
- Git can be used offline and does not need an internet connection to use unless we need to access the GitHub whereas GitHub cannot be used offline and needs an internet connection.
- Git is something independent and can be used without GitHub whereas GitHub has nothing to do unless we make repositories in Git.
- Git is focused on version control and code sharing while GitHub is focused on centralized source code hosting.
- Git doesn’t have a GUI while GitHub provides an easy to use GUI.
I hope the above information would be helpful for you to understand and get an idea about Git & GitHub!
Further Refer:
Get Started and Learn more!
As a next step, start using Git and try to create GitHub projects and start contributing to open source projects!
“Live as if you were to die tomorrow. Learn as if you were to live forever.” - Mahatma Gandhi
If you have any suggesions for improvements, let me know!